- What is Cloud Computing?
- Brief History of Cloud Computing
- Types of Cloud Computing Deployment Models
- Types of Cloud Services
- Top benefits of cloud computing
- Uses of Cloud Computing
- College Presentation
What is Cloud Computing?
Simply put, cloud computing is the delivery of computing services—including servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence—over the Internet (“the cloud”) to offer faster innovation, flexible resources, and economies of scale. You typically pay only for cloud services you use, helping lower your operating costs, run your infrastructure more efficiently and scale as your business needs change.
Brief History of Cloud Computing
- Old Mainframes & Mini Computers introduced idea of time-sharing & Client-Server Model. This terminology was mostly associated with large vendors such as IBM and DEC.
- In the 1990s, telecommunications companies, who previously offered primarily dedicated point-to-point data circuits, began offering virtual private network (VPN) services with comparable quality of service, but at a lower cost.
- In March 2006 Amazon introduced its Simple Storage Service (S3), followed by Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) in August of the same year.
- In February 2010, Microsoft released Microsoft Azure
- On March 1, 2011, IBM announced the IBM SmartCloud framework
- In May 2012, Google Compute Engine was released
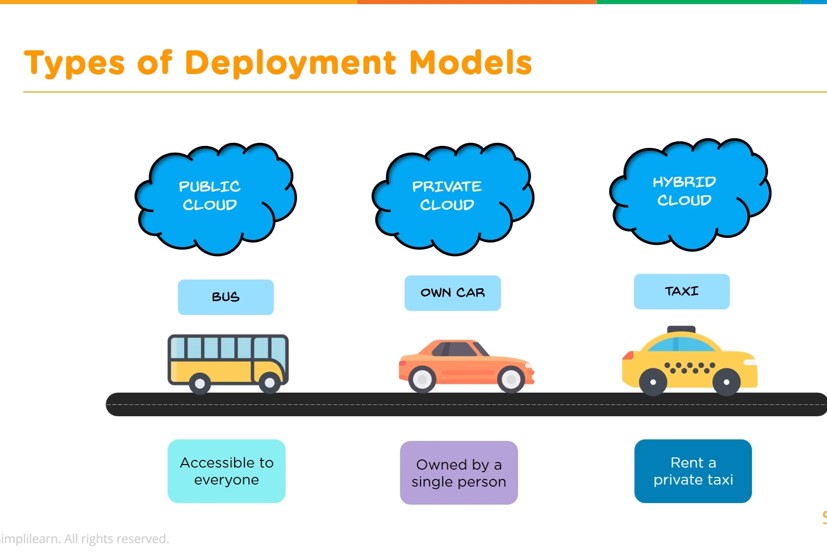
Types of Cloud Computing Deployment Models
Several different models, types and services have evolved to help offer the right solution for your needs. There are three different ways to deploy cloud services:
•Public cloud,
•Private cloud,
•Hybrid cloud
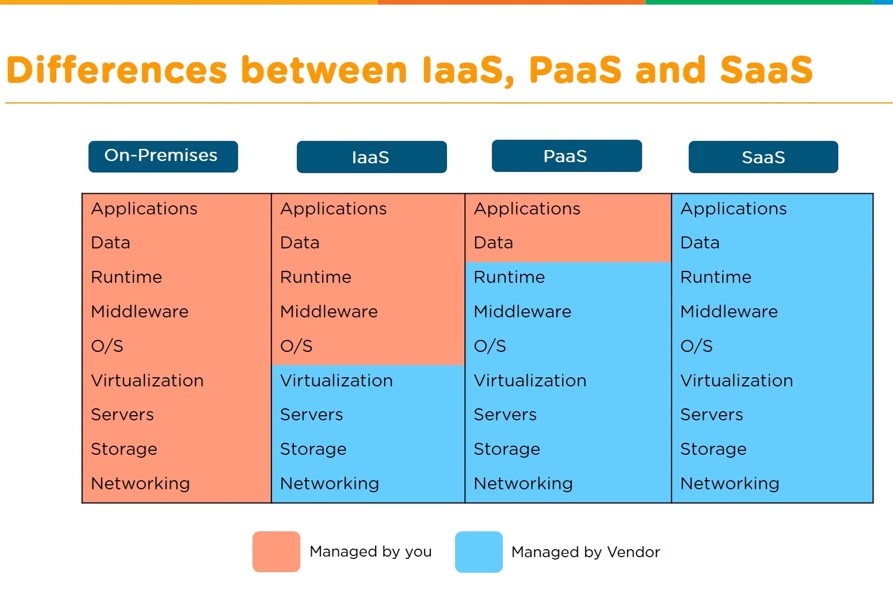
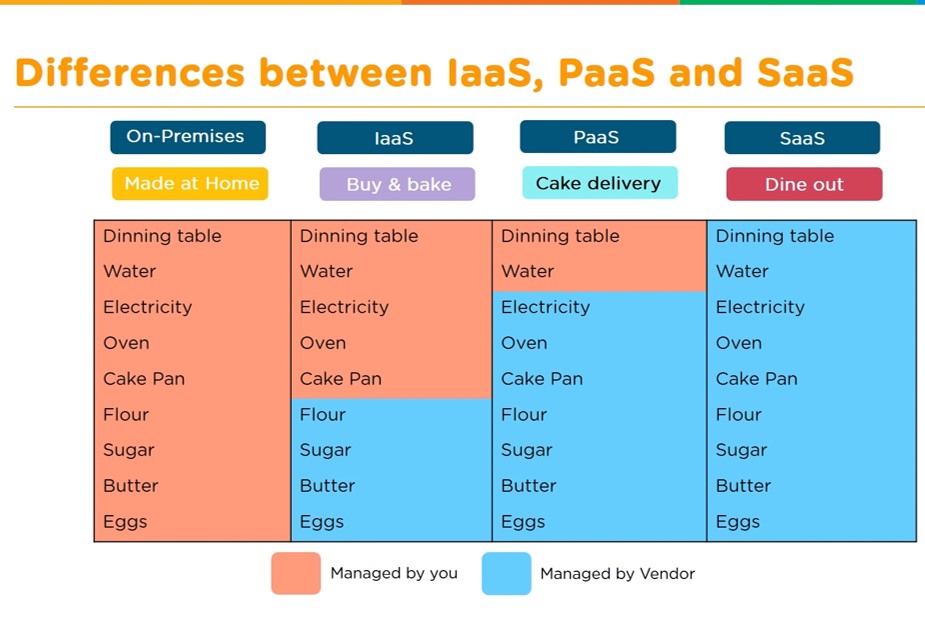
Types of Cloud Services
Most cloud computing services fall into four broad categories:
• Infrastructure as a service (IaaS),
• Platform as a service (PaaS),
•Serverless and
•Software as a service (SaaS).
These are sometimes called the cloud computing stack because they build on top of one another. Knowing what they are and how they are different makes it easier to accomplish your business goals.
Top benefits of cloud computing
•Cost- Cloud computing eliminates the capital expense of buying hardware and software and setting up and running on-site datacenters—the racks of servers, the round-the-clock electricity for power and cooling, the IT experts for managing the infrastructure. It adds up fast.
•Speed- Most cloud computing services are provided self service and on demand, so even vast amounts of computing resources can be provisioned in minutes, typically with just a few mouse clicks, giving businesses a lot of flexibility and taking the pressure off capacity planning.
•Global scale-The benefits of cloud computing services include the ability to scale elastically. In cloud speak, that means delivering the right amount of IT resources—for example, more or less computing power, storage, bandwidth—right when it is needed and from the right geographic location.
•Productivity-On-site datacenters typically require a lot of “racking and stacking”—hardware setup, software patching, and other time-consuming IT management chores. Cloud computing removes the need for many of these tasks, so IT teams can spend time on achieving more important business goals.
•Performance-The biggest cloud computing services run on a worldwide network of secure datacenters, which are regularly upgraded to the latest generation of fast and efficient computing hardware. This offers several benefits over a single corporate datacenter, including reduced network latency for applications and greater economies of scale.
•Reliability-Cloud computing makes data backup, disaster recovery and business continuity easier and less expensive because data can be mirrored at multiple redundant sites on the cloud provider’s network.
•Security-Many cloud providers offer a broad set of policies, technologies and controls that strengthen your security posture overall, helping protect your data, apps and infrastructure from potential threats.
Uses of Cloud Computing
•You are probably using cloud computing right now, even if you don’t realise it. If you use an online service to send email, edit documents, watch movies or TV, listen to music, play games or store pictures and other files, it is likely that cloud computing is making it all possible behind the scenes.
•The first cloud computing services are barely a decade old, but already a variety of organisations—from tiny startups to global corporations, government agencies to non-profits—are embracing the technology for all sorts of reasons.
•Create cloud-native applications-Quickly build, deploy and scale applications—web, mobile and API.
•Test and build applications-Reduce application development cost and time by using cloud infrastructures that can easily be scaled up or down.
•Store, back up and recover data-Protect your data more cost-efficiently—and at massive scale—by transferring your data over the Internet to an offsite cloud storage system that is accessible from any location and any device
•Analyse data-Unify your data across teams, divisions and locations in the cloud. Then use cloud services, such as machine learning and artificial intelligence, to uncover insights for more informed decisions.
•Stream audio and video-Connect with your audience anywhere, anytime, on any device with high-definition video and audio with global distribution.
•Embed intelligence-Use intelligent models to help engage customers and provide valuable insights from the data captured.
•Deliver software on demand-Also known as software as a service (SaaS), on-demand software lets you offer the latest software versions and updates around to customers—anytime they need, anywhere they are.
Complete Presentation
We have covered the basics of Cloud Computing above. You may download the complete ppt for full details. Download ppt.
You may also check Latest Updates on Microsoft Azure or check on Microsoft Session on MyBuild – Build cloud-native applications that run anywhere (microsoft.com)
College Presentation Video
A presentation was given on Cloud Computing by experts to the college students. A detailed Question Answer session was held thereafter. We followed it with few Practical Sessions on Basics of Microsoft Azure.

