Vision Institute of Technology, Kanpur
UNIT & YEAR WISE QUESTION
Unit-1
2010-11
- Explain open loop and closed loop controls with the help of suitable examples.
- Discuss the effect of feedback on the following :
Sensitivity
Stability
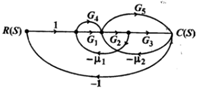
- Find the transfer function of the system shown in the 1 using Mason’s gain formula.
- Explain block diagram reduction technique to determine transfer function of a complicated
- Define the following
(a) Node loop (b) loop gain (c) path (d) forward path
2011-12
- Discuss the effect of feedback on the following 2011-12
overall gain stability noise & disturbance - Compare the open loop & closed loop control system
- Find the transfer function for the system whose block diagram representation is shown below.
- Define the following
(a) Node loop (b) loop gain (c) path (d) forward path (e) non touching loop - Write notes on (a) control valves (b) RTDs
2012-13
- Draw the electrical analogue of the mechanical system of fig. shown below.
- Find the transfer function of the system shown in the 1 using Mason’s gain formula.
- Draw the signal flow graph of the given block diagram & find the transfer function.
- How many types of feedback are there ? explain the advantages & disadvantages of each.
- What is the role of Sensors & encoders in control system . Explain the construction & principle of operation of potentiometer.
2015-16
- Compare between open loop and closed loop control system.
- What is techo generator?
- What is the general effect of adding a pole to the forward path transfer function?
- Define the following SFG terminology (1) Forward Path (2) Loop (3) Self Loop (3) Non touching Loop
- Determine the transfer function of the system shown in fig
- Discuss the effect of feedback on stability of the system.
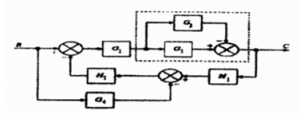
- Determine the overall transfer function of the given system below using block diagram reduction technique.

2016-17
- Distinguish between open loop and closed loop control system.
- Write the analogous electrical elements in FV analogy for elements of mechanical translational system.
- What sre the basic properties of signal flow graph.
- What is servomechanism?
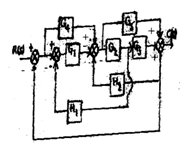
- Determine the transfer function C(S)/R(S) of the system shown in fig
- Derive the transfer function for the armature controlled DC servo motor.
- What is role of sensors and encoders in control system? Explain the construction and principle of potentiometer.
2017-18
- Define transfer function.
- Define non-touching loop
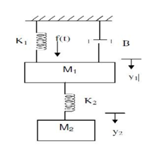
- Determine the transfer function Y2(S)/F(S) of the system shown in fig
- Find the overall gain of the system whose signal flow graph is shown in fig.
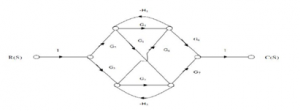
- Draw a signal flow graph and evaluate the closed loop transfer function of a system whose block is shown in fig.
2018-19
- Compare open loop and closed loop control systems.
- Define transfer function.
- Give Mason’s Gain formula.
- Write the analogous electrical elements in force voltage analogy for the elements of mechanical translational system?
- Why negative feedback is invariably preferred in closed loop system?
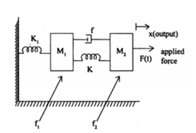
- Obtain the transfer functions of the mechanical systems and the analogous electrical circuit shown in the figure below:
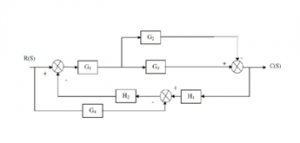
- Reduce the block diagram shown below to a single block and find the overall transfer function.
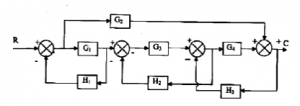
- Determine the sensitivity of the system given in the figure below with respect to feedback path transfer function at = 2.0
- A unity feedback system has an amplifier with gain Ka=10 and gain ratio G(S) = 1 / S(S+2) in the feed forward Path. A derivative feedback ,H(S)=SK0 is introduced as a minor loop around G(S).Determine the derivative feedback constant ,K0 ,so that the system damping factor is 0.6.
- Determine the overall transfer function from the signal flow graph shown in figure using the Mason’s gain formula.